
- #CMOS CHECKSUM INSTALL#
- #CMOS CHECKSUM UPGRADE#
- #CMOS CHECKSUM SOFTWARE#
- #CMOS CHECKSUM CODE#
- #CMOS CHECKSUM PC#
Now locate the CMOS backup battery and gently remove it from the motherboard. Power down and unplug the PC, then open the case and disconnect the power cables from the motherboard. But not every motherboard supplies this feature, so you may need to fix it the old-fashioned way.
#CMOS CHECKSUM UPGRADE#
This feature comes in handy if you need to clear a password or clean house after a BIOS upgrade (see " Clearing a Forgotten CMOS Password" earlier in this chapter). Most motherboards provide a jumper to clear the CMOS RAM. If you wait too long, the operating system will load. You only have a few seconds to start the Setup routine. For example, you will see a message like “Press to enter Setup” (see Table 1-1). Most BIOS will show you the proper key to press on the screen in the moments following startup. Once you know the trick, you can easily get into the Setup routine. In fact, a little coin cell powers the CMOS RAM when you turn off the PC. A small amount of very low-power CMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) RAM stores each variable. Part of the BIOS includes a Setup (or System Setup) routine that lets you define the hardware particulars (you can see a few example Setup menus in Figures 1-6 and 1-8). However, BIOS instructions must adjust for various hardware configurations (such as memory speed and I/O port availability).
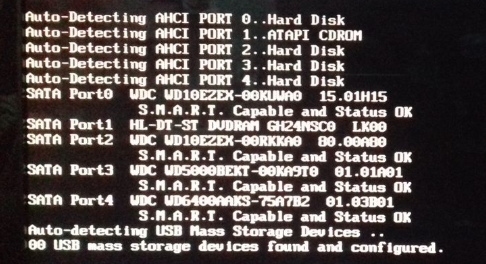
This is often called firmware because the BIOS instructions are recorded on the chip itself.

#CMOS CHECKSUM PC#
To set the record straight, the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a motherboard chip that stores the instructions needed to boot your PC and transfer control to the operating system. The sequence of POST is system-specific.The computer industry often uses these related terms interchangeably. Generally, the order of initialization is Processor -> Memory -> Busses -> Output/Input Devices -> Boot Devices. The early codes are for subsystems closer to the processor and the later codes are for peripherals.
#CMOS CHECKSUM CODE#
Port 80h code values typically increase during the boot process. Reserved for future use (new input console codes)īoot Devices: Includes fixed media and removable media. Reserved for future use (new output console codes) I/O Busses: PCI, USB, ISA, ATA, and so on. Started dispatching PEIMs (emitted on first report of EFI_SW_PC_INIT_BEGIN EFI_SW_PEI_PC_HANDOFF_TO_NEXT)ĮFI boot service ExitBootServices ( ) has been calledĮFI runtime service SetVirtualAddressMap ( ) has been calledĮFI runtime service ResetSystem ( ) has been calledĭebug codes: Can be used by any PEIM/driver for debug Unrecoverable input device (keyboard or mouse) errorĭetecting presence of a fixed media (IDE hard drive detection, and so on.)ĭetecting presence of a removable media (IDE, CD-ROM detection, and so on.) Instructing keyboard controller to run Self Test (PS2 only) (On a 7-segment LED display, the 'b' looks like a 6). If you see a POST code in this range, it should be read as B0 - BF. There are currently no valid POST codes in the 60 - 6F range. I/O Busses (PCI, USB, ISA, ATA, and so on.) Handing off control to the recovery capsule
#CMOS CHECKSUM SOFTWARE#
No memory detected or no useful memory detectedĬrisis Recovery has initiated per User requestĬrisis Recovery has initiated by software (corrupt flash) Programming timing parameters in the memory controller and the DIMMs Starting Application processor initialization Host processor Cache initialization (including APs) Power-on initialization of the host processor (Boot Strap Processor) POST Codeĭebug Codes: can be used by any PEIM/driver for debug This code can be used to find out why the error occurred. If the POST fails, the last POST code generated is left at port 80h.
#CMOS CHECKSUM INSTALL#
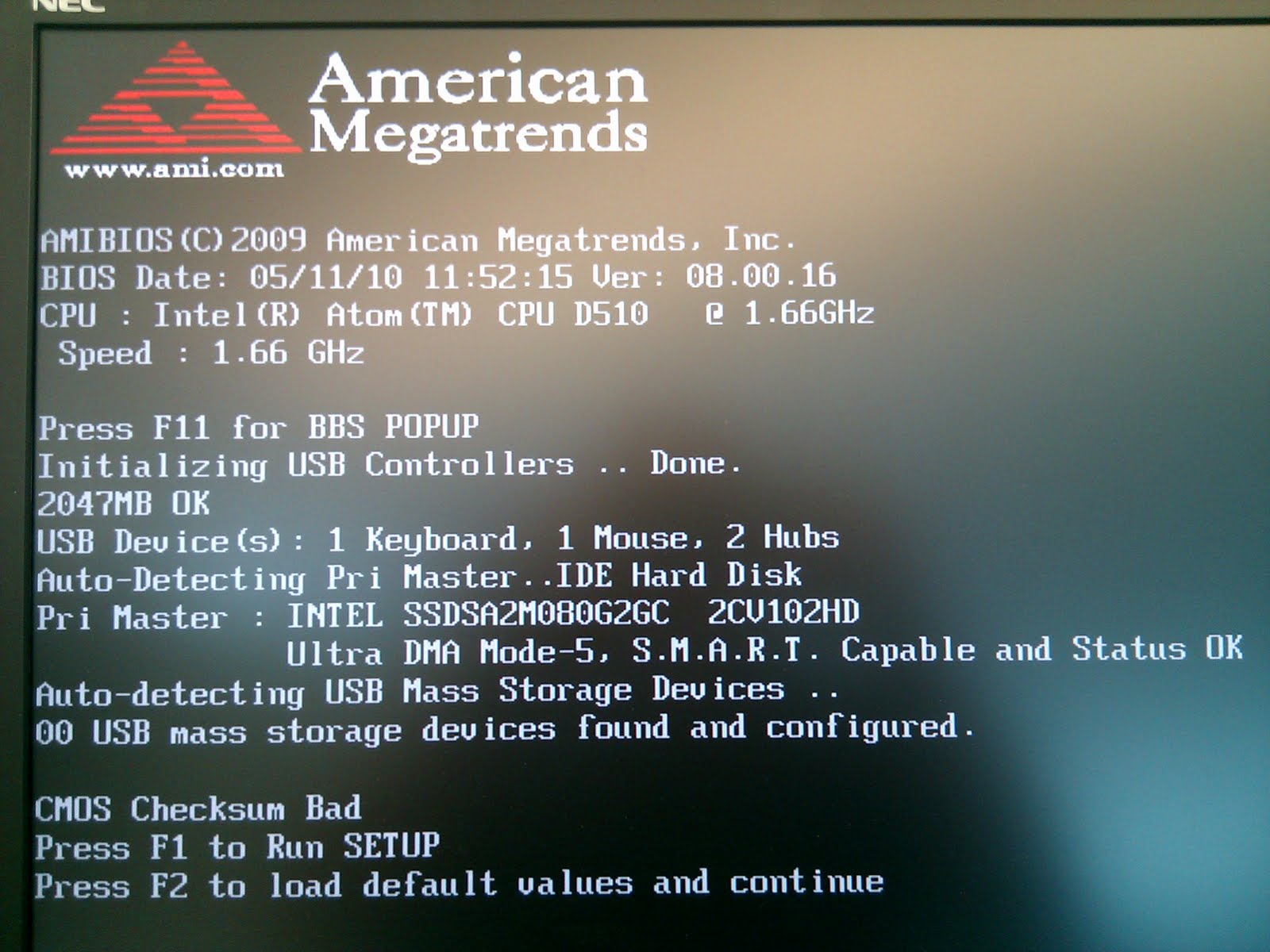
If no memory was removed, the memory might be bad. Memory size has decreased since the last boot. Press F2 during boot to enter BIOS Setup.

Try the following:ĭownload and install the latest BIOS version for your Intel NUC. In the tables below, POST codes and range values are in hexadecimal. This document defines the error messages and POST codes that could be seen when starting an Intel® NUC.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
